
Nodal Analysis
Related Term
Nodal analysis is a method that provides a general procedure for analyzing circuits using node voltages as the circuit variables. Nodal Analysis is also called the Node-Voltage Method.
Some Features of Nodal Analysis are as
-
Nodal Analysis is based on the application of the Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL).
-
Having ‘n’ nodes there will be ‘n-1’ simultaneous equations to solve.
-
Solving ‘n-1’ equations all the nodes voltages can be obtained.
-
The number of non reference nodes is equal to the number of Nodal equations that can be obtained.
Types of Nodes in Nodal Analysis
-
Non Reference Node - It is a node which has a definite Node Voltage. e.g. Here Node 1 and Node 2 are the Non Reference nodes
-
Reference Node - It is a node which acts a reference point to all the other node. It is also called the Datum Node.
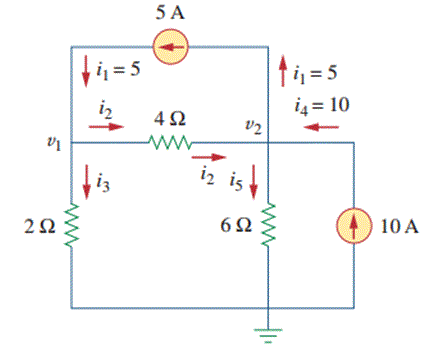
Step I. Assign the nodes voltages as v1 and 2 and also mark the directions of branch currents with respect to the reference nodes
Step II. Apply KCL to Nodes 1 and 2 KCL at Node 1 KCL at Node 2 Step III. Apply Ohm’s Law to KCL equations • Ohm’s law to KCL equation at Node 1 Simplifying the above equation we get, • Now, Ohm’s Law to KCL equation at Node 2 Simplifying the above equation we get Step IV. Now solve the equations 3 and 4 to get the values of v1 and v2 as, Using elimination method And substituting value v2 = 20 Volts in equation (3) we get- Hence node voltages are as v1 = 13.33 Volts and v2 = 20 Volts.